Exploring Role of Adipose Organ and Dysmetabolic Effects of Adiposity: Over-Nutrition, Nutrient Overload, Insulin Resistance, T2DM and Other Fallouts By Vinod Nikhra* in Research in Medical & Engineering Sciences_ Journal of Medical Sciences
Introduction
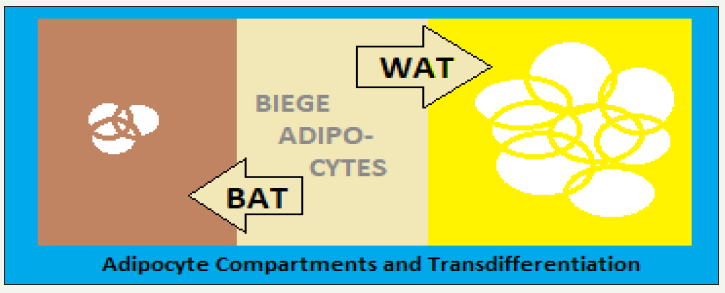
The complex adipose organ
It has highly plasticproperties to reprogram its
genes and transdifferentiate reversibly into cells with different structure and
functions.The adipose organ plays important role in health and disease states
including obesity and MetS and fulfils several crucial survival needs like
thermogenesis, storage of energy and fuel for metabolism, immune responses,
sexual development around puberty, reproductive function and lactation.
Further, as an endocrine organ, it secretes several peptides termed adipokines,
including adiponectin and leptin.
Adiposity and metabolic
mechanisms
The rising prevalence of obesity and MetS in
recent decades reflects increased calorie consumption though diets rich in fat
and refinedcarbohydrates,
leading to over-nutrition and nutrient overload which in due course leads to
nutritional toxicity, endangering the intracellular organelle and impairing
intracellular and intercellular metabolic processes. The adipose tissue
protects the vital organs through expansion of the WAT, through an upsurge in
the adipocytecellsize and formation of new white adipocytes, and adiposity can,
thus, be regarded a way to deal with nutritional excess.The IR linked to
adiposity can also be regarded a measure to control excess nutrients entry into
cells, endangering vital intracellular organs.
The excess folic acid and
obesity link
Folic acid influences energy aswell as lipid
metabolism by modifying DNA synthesis and gene expressions and contributes to
alterations in metabolism. In the animal
model, the EFA with a HF diet were related to significant weight and fat
mass gain. Thus, EFA may intensify weight increase, adiposity and inflammatory
response in setting of increased fat dietary intake.
Metabolic fallouts of
adiposity/obesity
The adipose tissue relates to about 20% of body
weight in lean individuals and to 50% or more body weight in extremely obese.
The adipose tissue organ has white, beige and brown adipocytes for specialized
functions, and their coordinated action ensure an optimal metabolic
homeostasis. The adiposity is a crucial factor in development of metabolic
diseases including DM, and high BMI, T2DM and IR are closely linked.With
obesity, the levels of NEFAs, adiponectins,
cytokines and proinflammatory markers like NNF-α and IL-6 involved in the
genesis of IR, are increased, and with metabolic dysfunctions, there occur
derangements of carbo-lipid and global metabolic homeostasis. Normally, there
is a dynamic feedback relationship between β-cells function and insulin-sensitive
response in tissues. The failure of the intricate process and sustained decline
in β-cell function result in dysregulation of glucose levels and worsening
ofT2DM.
Future projections and
options
Both obesity and T2DM represent a global public
health crisis brought about by rapid westernization, nutritional alterations
transition and increasingly sedentary lifestyles. Controlling and treating
Obesity as well as T2DM and their fallouts require a thoughtful long-term
planning and rational use of limitedresourcesin developing countries with
scarce resources. Further, owing to the wide range of therapeutic interventions
and options available, the treatment algorithm is ridden with complexity.
https://crimsonpublishers.com/rmes/fulltext/RMES.000627.php
For
more Open access journals in Crimson Publishers,
Please
click on the link: https://crimsonpublishers.com/
For
more articles in Journal of
Medical Sciences,
Please
click on below link: https://crimsonpublishers.com/rmes/
Follow
On Publons: https://publons.com/publisher/6342/crimson-publishers/
Follow
On Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/company/crimsonpublishers/
High
impact journals in Crimson Publishers?
https://www.quora.com/What-are-the-high-impact-journals-in-Crimson-Publishers
Crimson
Publishers Journals
https://crimsonpublishers.com/



No comments:
Post a Comment