Dexmedetomidine as a Sole Sedative Agent versus Propofol for Sedation during Upper and Lower Gastrointestinal Endoscopies by Alaa Ali Elzohry* in Developments in Anaesthetics & Pain Management_ Research and Reviews International Journals
Introduction
Introduction
and objectives: Diagnostic and therapeutic procedures recently are done in
gastroenterology setup as a part of fast-track concept. A major volume of
gastrointestinal procedures are performed routinely on daycare basis under
sedation as upper and lower GIT endoscopy. Many anesthetic agents used to
provide sedation for these procures. Propofol, opioids, and midazolam form the
backbone of the various regimes
employed in the endoscopic suites all over the world. Dexmedetomidine is a
pharmacologically active selective α 2-adrenergic receptor agonist. It was
approved it in the intensive care unit (ICU) for sedation and analgesia for the
duration of less than 24 hours. The aim of this study was to study efficacy and
safety of Dexmedetomidine efficacy as sole sedating agent versus propofol for
sedation during upper and lower GIT endoscopy.
Methods:
This randomized controlled trial was carried out on 60 patients of either sex,
aged 21-70 years of age undergoing upper and lower GIT endoscopy, with ASA
I-II. Patients were randomly assigned into two groups, (30 patients in each
group).
Dex
group: Sedation was induced by loading dose of (dexmedetomidine 1μg/kg)
followed by infusion of (dexmedetomidine 0.8μg/kg /h) Propofol group: Sedation
was initially started by bolus dose of 0.5mg/kg propofol IV Then, infusion was
started at the rate of 50μg /kg/min. Upper and lower GIT endoscopies were
carried out in the usual standard manner for all patients, then patients were
discharged to PACU after
attaining an Aldrete Recovery Scale Score of 9-10 Time taken to achieve this
score was recorded. The patient’s vital signs, Respiratory complications, VAS
score for pain measurement, PONV, and any other adverse events were recorded.
Results:
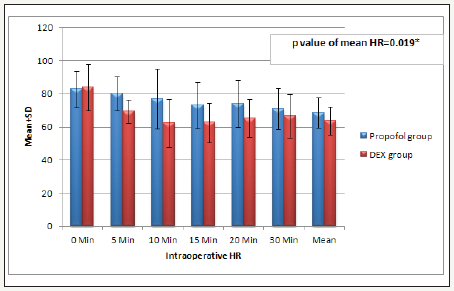
There was significant decrease in (HR and MAP) but not respiration rate (RR)
and SpO2, in (Dex group) during the procedure and early post-operative (P.
value 0.000**). But during the remaining of post-operative periods (HR and MAP)
were comparable. VAS pain scores in both groups were decreased in comparable
manner at all measured time points. But complications (atthythmia, air way
obstruction, nausea, and vomiting) was significantly increased in Propofol
group (P. value 0.001**). Mean time to achieve RSS 3-4 was 6 (±1.5) min in Dex
group versus 9 (±1.9) min in Propofol group (P< 0.005) and to achieve an
Aldrete Recovery Scale Score of 9-10 was 8 (±2.1) min in Dex group versus 6 10
(±1.6) min in Propofol group (P< 0.029).
https://crimsonpublishers.com/dapm/fulltext/DAPM.000520.php
For
more articles in Research and Reviews
International Journals,
Please
click on below link: https://crimsonpublishers.com/dapm/



No comments:
Post a Comment